xThis page describes the Intent Based Network.
Use Case Name
Primary Contacts:
BUSINESS DRIVER
This section describes Business Drivers needs.
EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
The Intent-based Network (IBN) is available to bridge the gap between the business department and IT department. It is able to capture the intents of business sensitively, and then reconfigure the end-to-end network according to the intents momentarily. Normally, the operation of underlay network and related systems are involved when opening or reconfiguring a network service. It needs professionals of different roles to perform a series of complex operations, which also takes a long time. The target of IBN is to establish an extensible framework to identify the users' network requirements based on natural language, allocate appropriate resources with the help of preset business knowledge or self-learning intelligent engine, and then convert them into the operations of network equipment and interface automatically, so as to simplify the operations.
In addition, the IBN also includes:
(1) Intent verification function: It is used to verify whether the automatically created network services satisfy the requirements of users;
(2) Intent assurance function: With the help of periodic analyzed business KPI, it checks whether the current network services satisfy the users' requirements, such as QoS. If not, it will reconfigure the resources and networks to satisfy the expectations of users.
BUSINESS IMPACT - The Internet of Everything will be true not soon later. The IBN has great potential in the applications from users and devices in the park or branch office to the data center or cloud. It is able to reconfigure and optimize the network continuously, protect IT and business processes, and provide insight. The IBN simplifies the operation of opening and reconfiguring network service, as well as the operation of monitoring and assuring network quality after opening the service. Operators can use the IBN to capture the intents of business, and then monitor network status and implement strategies in the whole networks. It is able to satisfy the requirements of network business much better.
BUSINESS MARKETS - The Intents can be applied to multiple levels, such as application service levels, security policies, compliance transactions, operational processes and other business requirements. The IBN will be applied to the scenes of the opening and management of various network services. In the first stage, it will be used in the 5G use case to opening and monitoring of network services. Later, it will be integrated into more use cases to simplify the opening and management of services.
FUNDING/FINANCIAL IMPACTS - The IBN is able to respond to the requirements of organizations quickly with little human intervention. with the corresponding reduction of time and energy required for network maintenance, IT professionals can spend more time on innovation to bring practical value to the enterprise. The IBN is able to respond to the requirements of organizations quickly, simplify the manual operation of network opening and management, and reduce operators' OPEX.
ORGANIZATION MGMT, SALES STRATEGIES - There is no additional organizational management or sales strategies for this use case outside of a service providers "normal" ONAP deployment and its attendant organizational resources from a service provider.
Development Status
| PROJECT | PTL | User Story / Epic | Requirement |
| A&AI | |||
| AAF | |||
| APPC | |||
| CLAMP | |||
| CC-SDK | |||
| DCAE | |||
| DMaaP | |||
| External API | |||
| MODELING | |||
Multi-VIM / Cloud | |||
| OOF | |||
| POLICY | |||
| PORTAL | |||
| SDN-C | |||
| SDC | |||
| SO | |||
| VID | |||
| VNFRQTS | |||
| VNF-SDK | |||
| CDS |
List of PTLs:Approved Projects
*Each Requirement should be tracked by its own User Story in JIRA
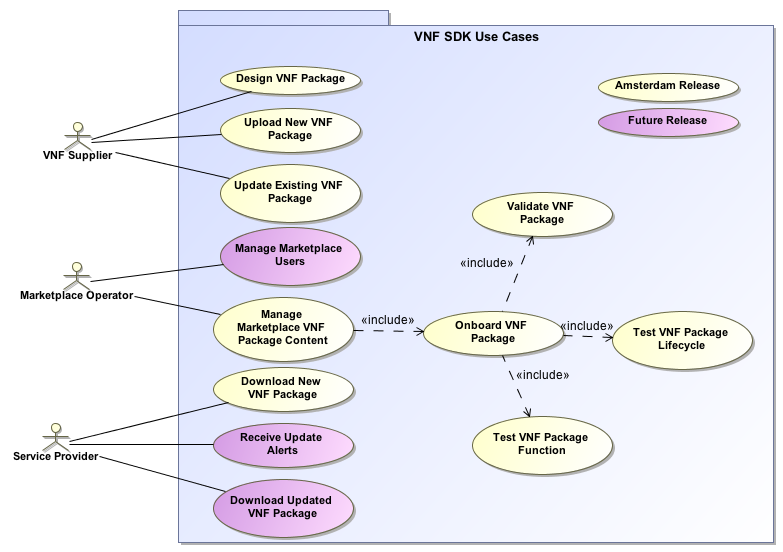
Use Case Diagram
Use cases define how different users interact with a system under design. Each use case represents an action that may be performed by a user (defined in UML as an Actor with a user persona).
Use Case Functional Definitions
Use Case Title | Title of the Use Case |
Actors (and System Components) | The list of Actors and System Components that participate in the Use Case |
Description | Short overview of the Use Case |
Points of Contact | Authors and maintainers of the Use Case. Use Case Lead, Key Use Case members and code contributors. |
Preconditions | A list of conditions that are assumed to be true before the Use Case is invoked Includes description of Information Consumed |
Triggers / Begins when | Describes the trigger for beginning the Use Case |
Steps / Flows (success) | Describes the sequence of steps and interactions that occur during the Use Case (may include: description, data exchanges, functionality, state changes) Interaction diagrams may be included or referenced |
Post-conditions | The expected results of the execution of the Use Case Includes description of Information Produced |
Alternate / Exception Paths | Description of any exceptions or special process that could occur during Use Case |
Related Use Cases | List of the Use Cases referenced by this Use Case |
Assumptions | Describes any assumptions that are made for this use case |
Tools / References / Artifacts | List of any tools or reference material associated with this Use Case as well as any JIRA trace-ability. List of any associated diagrams or modelling artifacts associated with the Use Case |
Testing
Current Status
Testing Blockers
- High visibility bugs
- Other issues for testing that should be seen at a summary level
- Where possible, always include JIRA links
End to End flow to be Tested
**This should be a summary level Sequence diagram done in Gliffy**
Test Cases and Status
| 1 | There should be a test case for each item in the sequence diagram | NOT YET TESTED |
| 2 | create additional requirements as needed for each discreet step | COMPLETE |
| 3 | Test cases should cover entire Use Case | PARTIALLY COMPLETE |
| 4 | Test Cases should include enough detail for testing team to implement the test | FAILED |